![]()
R0=Nt+1 / Nt
I. Review of population growth models
Density-independent population growth models
Density-dependent population growth models
Age-structured, density-independent population models
Stage-structured, density-independent population models
II. Special cases for small populations
III. Advanced concepts for small populations
A. Discrete generation
1. Assumptions
2. Definitions
![]()
R0=Nt+1 / Nt
To project population under the assumptions of this model:
Nt = N0 R0t
R > 1 => population is growing
R = 1 => population size is constant
R < 1 => population is declining
When would density-independent growth be applicable to conservation cases?
Perhaps invasive species.
B. Continuous growth
1. Assumptions
a. Same as above
b. Both discrete and overlapping generations grow exponentially, when growth is positive
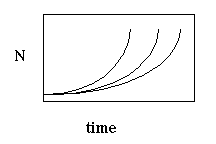
2. Definitions
a. Change in population size can be defined as:
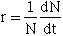
--where r is referred to as the intrinsic rate of increase
b. r = b - d where b = instantaneous birth rate and d = instantaneous death rate
![]()
3. Logistic equation is derived from above equation:
![]()
4. Calculation of r:
a: Using the equation below, plot N versus t on semi-log paper.
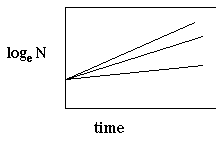
b. Slope is r.
c. Notice:
![]()
A. Verhulst (1838) equation
![]()
1. Note that change in population size is a function of N and K.
2. Known as logistic equation
3. Integrated form of equation :

4. Change in population is at its maximum at intermediate population size. (see example below)
5. Allele effect occurs at low N
Example: Bacteria population with K=100, r=1.0, N0=1
| Population size (Nt) | (K-N)/K |
dN/dt (rate of pop. growth) |
| 1 | .99 | .99 |
| 50 | .50 | 25.0 |
| 75 | .25 | 18.75 |
| 95 | .50 | 4.75 |
| 99 | .01 | .99 |
| 100 | .00 | 0 |
Note that the change in population growth rate over time is fastest at intermediate population sizes.
Issues for conservation:
A. Life tables
1. Definition: age-specific mortality schedule of a population
2 Critical parameters:
a. age interval
b. age specific survival
c. age specific fecundity
3. Example
| age, x | Number of individuals | survival, lx | age-specific survival, lx | age-specific fecundity |
| 0 | 150 | 1.0 | .5 | 0 |
| 1 | 75 | .5 | .4 | 1.5 |
| 2 | 30 | .2 | 0 | 2 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 |
3. Types of life table
a. Cohort: generational; survivorship based on a single cohort over time.
b. Static (vertical): survivorship based on multiple age classes sampled at one point in time.
c. modified cohort: cohort of individuals is monitored for 1-many years.
4. Information estimated from life tables:
a. age-specific life expectancy: average number of years to live for an individual of age x.
b. age-specific reproductive value: Relative number of offspring that remain to be born to individuals of a given age.
c. Net Reproductive Rate (R0) average number of female offspring produced by each female during her lifetime.
![]()
B. Population matrices
1. Life table information is summarized into a matrix
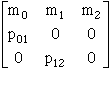
2. Using data from example above, we can construct the following matrix.

3. Using matrix algebra, we can calculate the population growth rate: determine that the following matrix has
l = er = 1.0615
r=ln l = 0.0597
A. Life table information
1. stages in organisms life
a. insect: egg, pupa, n-star
b. birds: eggs, fledglings, juveniles, non-reproductive adults, reproductive adults
c. Plant: seed stage, seedling stage. sapling stage. juvenile, adult
B How to collect data:
1. Modified cohort
a. Parameters are measured yearly at appropriate time
b. Summarized in terms of stage-specific transition probabilities.
2 . Example of stage-structured data
| stage | probability of going to next stage | probability of staying in same stage | stage-specific fecundity |
| seeds | .50 | 0 | 0 |
| seedlings | .20 | .40 | 0 |
| saplings | .25 | .50 | 0 |
| juveniles | .10 | .70 | 10 |
| adults | 0 | .95 | 100 |
C. Stage projection matrix
1. Constructs a matrix from transition probabilities
2. Matrix from table above:
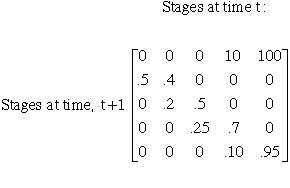
3. Dominant eigen value of this matrix = l = 1.3845
Applications of life table approach for conservation:
Focus on critical phases in life cycle where impact of disturbance is occurring most dramatically
 PHOTO BY taken from http://www.sfu.ca/biology/faculty/williams/ebird/credits.html
PHOTO BY taken from http://www.sfu.ca/biology/faculty/williams/ebird/credits.html
When population is large, positive relationship between population density and the reproduction and survival of individuals
When population is small, increased difficultly of finding mates or reproducing at low population size.
A special form of density-dependence



Aster furcatus , Forked aster: understory plant: found at fewer than 50 sites in six Midwest states, is classified as threatened in Illinois.
Gentiana pneumonanthe, European understory shrub.
Both species have incompatibility systems: